The average Reps for pull ups various person to person. There are soo many factor which comes in such as workout goals, age, level of strength, endurance, gender and more. Below, all the factors will be considered in a chart form.
Pull up is a compound move which targets the upper body to work. It’s best to know which muscle is being targeted, which are:
- Lats – Primary
- Upper Back
- Traps (Trapezius)
- Pecs (Pectoralis major)
- Arms (Biceps)
- Shoulders (Teres Major)
- Forearms
- Abdominals
(Check the muscle group in more detail)
So what is the Average reps for Pull ups is?
The Average Pull up reps for Men is 8-20 reps.
The Average Pull up reps for Women is 3-12 reps.
Average Pull up Category Chart Men
| Category | Average Reps |
| Beginner | 1 – 4 Reps |
| Intermediate | 5 – 12 Reps |
| Advanced | 13 – 25 Reps |
| Elite | 26 – 50 Reps |
Average Pull up Category Chart Women
| Category | Average Reps |
| Beginner | 1 – 3 Reps |
| Intermediate | 4 – 8 Reps |
| Advanced | 9 – 13 Reps |
| Elite | 14 – 25 Reps |
Must Read:- 10 Essential Back Machines for Building Back Muscle
How many Pull ups should I do a day ?
After Performing pull ups every day for some time, you need to know how many pull ups you should perform a day. The answer various person to person as we all have different level pull up fitness.
If you’re new(Beginner) to pull ups then you should do 1-2 pull ups everyday for 3 sets. So, it’s 3-6 pull ups in total.
If you’re doing pull ups for some time (Intermediate) then you should do 3-8 pull ups everyday for 3 sets. So, it’s 9-24 pull ups in total.
If you’re doing pulls regularly (advanced) then you should do 9-20 pull ups everyday for 3 sets. So, it’s 27-60 pull ups in total.
If you’re a pro(elite) at pull ups then you should be do 21-50 pull ups everyday for 3 sets, So it’s 63- 150 pull ups in total.
Benefits of Pull Ups

Pull ups exercise have soo many benefits like physical health, appearance, building muscle, improving mood.
Improve over Physical health
Pull up exercise can be very beneficial to your overall health. As 2012 study shown resistance training has improved overall health. All of it connect to better overall physical performance, control of movement, walking speed, and cognitive ability.
Builds Upper body Strength
Pull up is a compound exercises which help improves balance, react tine and coordination. Most of the tension is on the upper body which makes it a great exercise for the upper body. One of best exercise for working the whole upper body.
No Strain to the Joints
Pull up is a low-impact exercise which help build strength and no strain to the joints.
Good for mental Health and Mood
A 2010 study shows that strength training exercises help with depression, sleep, anxiety and fatigue, and cognition in older adults.
How to increase your pull up?

1) Strengthen Upper body muscle such Shoulders, Arm Muscle, etc.
As you already know, Pull up is a compound movement. It required different part of your upper body muscle to work together. You may be finding it difficult to perform pull ups due lack of shoulder and arms strength.
Train your upper body regularly, you can even train them at the end of your workout everyday.
2) Improve your core
When performing pull ups the abdominal muscle are used to keep the torso and legs stable during the pull up. During low-rep sets, the abdominals are activated more than any other muscle.
Train your core by doing some abdominal exercises regularly or at the end of the workout.
3) Hang on bar to increase your forearms and Grip strength.
Doesn’t matter if you’re pulling or pushing, Grip and Forearms strength is very important when it comes to any compound exercises.
Train your grip and forearms by doing grip exercises regularly or at the end of the workout.
4) Use resistance bands
Resistance bands can be very useful when it comes to increase your pull ups. All resistance bands does is assist you with your pull ups. Over time you will build strength and correct form with your pull ups will be able to more reps without the resistance band.
An alternative for this it to use assisted pull up machine as it will also help you without form and build strength over time if performed correctly and regularly.
How to do a pull up with correct form?
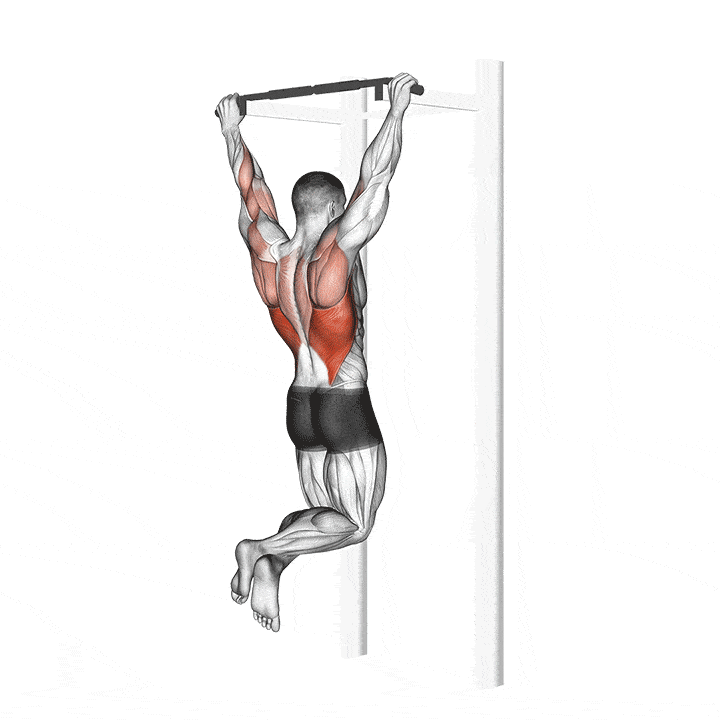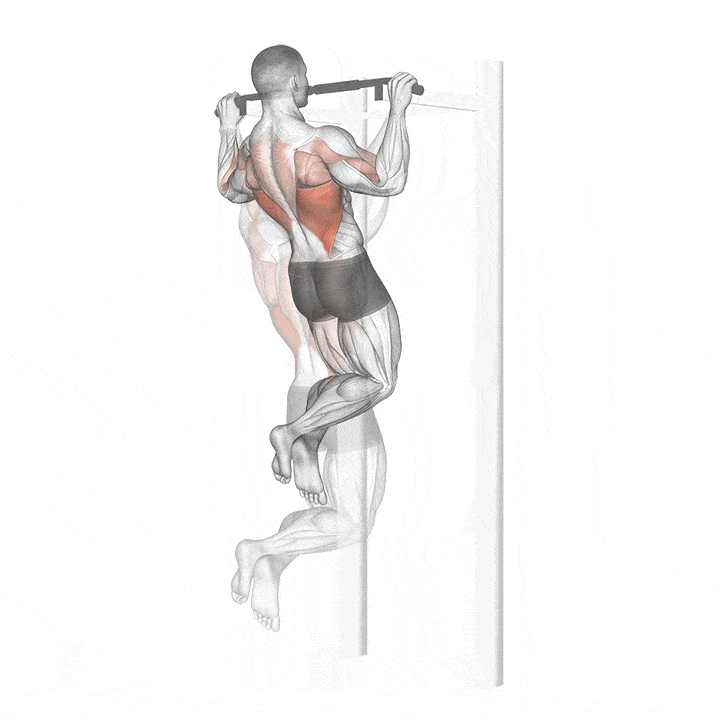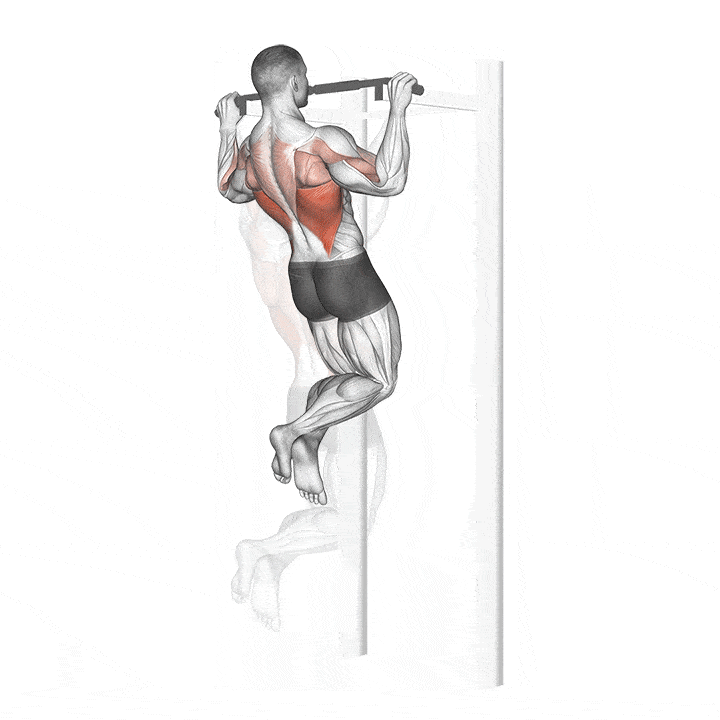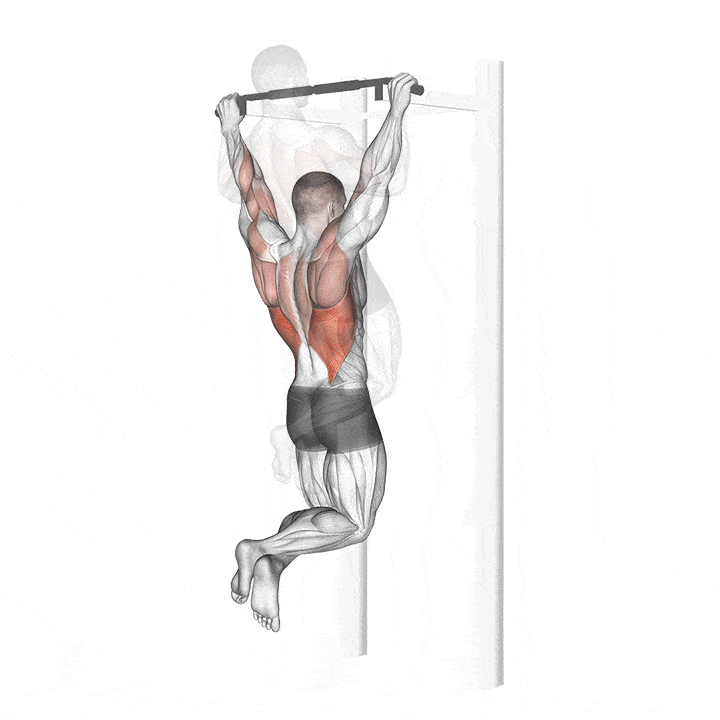
STEP 1 – Stand below a pull-up bar.
STEP 2 – Keep your Hand shoulder width apart and place your hand in an overhand grip.
STEP 3 – Jump and grab the bar like your hanging. This is the starting position.
STEP 4 – Inhale, then exhale. Engage your core by pulling your belly button toward the spine and pull the shoulders back and down.
STEP 5 – Raise your upper body toward the bar as you bend the elbows using your arms and back muscle (making sure your chin is over the bar) You can imagine bringing your elbows toward your hips if that makes the movement easier.
STEP 6 – Avoid swinging legs and shrugging the shoulders up. Ensuring that the shoulder blade remain back down throughout the exercise.
STEP 7 – Inhale and then have your elbow and body back down to the starting position.
Pull-Ups vs. Chin-Ups
Pull ups and Chin ups are both effective workout for training the upper body. The main difference is the position of the hand. With pull ups, you’re using overhand grip where your hand is facing away from you which primarily target your lats and upper back muscle. With chip ups, you’re using underhand grip where your hand is facing towards you (like a bicep curling position) which primarily targets biceps and chest muscle.
Supportive machine exercise to help you pull up
1) Lats pull-down
Lats pulldown back machine is recommended for building back muscle. Aesthetically, it will give the wings/V-shape and bigger lats will make your waist look smaller. Not only that, having stronger Lats helps stabilized the neck, shoulders and back.
2) Straight Arm Pulldown Machine
Straight Arm Pulldown machine is a great exercise when focusing on your upper back and lats. This back machine will help you get a wider and thicker back. When doing this exercise you need to ensure your form is correct.
3) Front Pull Down Machine
Front pull down works the latissimus dorsi muscle (broadest muscle of the back, also known as lats) through the downward rotation and depression of the scapulae (shoulder blade), thus targeting the back width.

