Squats are a great exercise when it comes to targeting the lower back, legs and core. It is performed to help people, build leg muscle, maintain muscle, burn fat and tone up. The most important thing you must about squats is that they are not just for bodybuilders or weight lifters anyone who wants to tone up can do it anywhere and any time without any specific equipment. Make sure you’re performing squats correctly otherwise it can cause injury.
The average Squat for a 14-year-old varies from person to person. It comes down to the person’s weight and height. For example, some 14-year-olds might be able to squat 60kg some might not. Check average height to bodyweight chart.
So How Much Should A 14-Year-Old Be Able To Squat?
Answer: The average squat for 14-year-olds is 1 times body weight. Squats range from 99 – 143 lb (45kg to 65kg) for 14-year-olds depending on the weight class.
When you bend to pick up something or tie your shoelaces from the floor, you are squatting. The only dissimilarity between those movements and squatting exercises is that while doing squat exercises, you intentionally hold the right posture to gain some planned advantage. You can do squat exercises with or without weights. Either way will help you, and adding weights will lead to advancements in general muscle mass. Yet, if you use weights then you must know how to squat perfectly to avoid harm.
People who squat without proper form may undergo knee pain. They can control this by assuring that the knees remain in line with the feet during the squat. Squatting with weights can raise the chance of injury which includes injury to the knees or lower back when a person does not do the exercise precisely. Anyone performing weighted squats for the first time must consider the recommendation of a trainer.
We recommend this belt as it will provide protection to your Lower back when performing Heavy Squats

Average Squat Chart for 14-year-Old
| BODYWEIGHT | BEGINNER | INTERMEDIATE | ADVANCED |
|---|---|---|---|
| 99 – 120 Lb (40.8 – 54 Kg) | 49.5 – 60 Lb (18.5 – 27 Kg) | 99 – 120 Lb (40.8 – 54 Kg) | 124 – 150 Lb (56 – 68.5 Kg) |
| 121 – 140 Lb (54 – 63.5 Kg) | 61 – 70 Lb (27 – 31.7 Kg) | 121 – 140 Lb (54 – 63.5 Kg) | 151 – 175 Lb (68.5 – 79 Kg) |
| 141 Lb + (64 Kg)+ | 70 Lb + (32 Kg)+ | 141 Lb + (64 Kg)+ | 176 Lb+ (79Kg) + |
- Must read:- Average Dumbbell curls for 14-year-old
- Must read:- Average Bench Press for 14-year-old
- Must read:- Average Deadlift for 14-year-old
Average 14-year-old squats for Beginner
Average 14-year-old squats for beginners is half of your bodyweight. For example, if you weigh 50Kg then you should be able to squat 25 kg. However, if you cannot squat your own body weight then it indicates that you’re weaker in your lower body.
Warming up is necessary before squatting. This can be done by doing 10 mins of cardio and 5 minutes of stretching will ease your muscles, expand your range of motion, and help control injury. The number of squats you should do has nothing to do with your gender and everything to do with your fitness level. Be aware of your limitations and make sure your form is stable before adding extra weight or reps.
Although squats are a surprisingly useful exercise, they are not an essential element. Combining them into a full-body workout control and eating the good things in the right amounts will give you the most satisfactory results. As a beginner, squatting 3 sets of 12-15 reps many times a week is great for you to more muscle and fuller jeans.
In squatting, women retained their upper bodies more erect than men, who leaned their upper bodies forward. By the laws of gravity, both men and women must keep their centre of mass straight above the supportive foot to stay in balance. Both do so, but men and women do it differently.
How to perform Squats
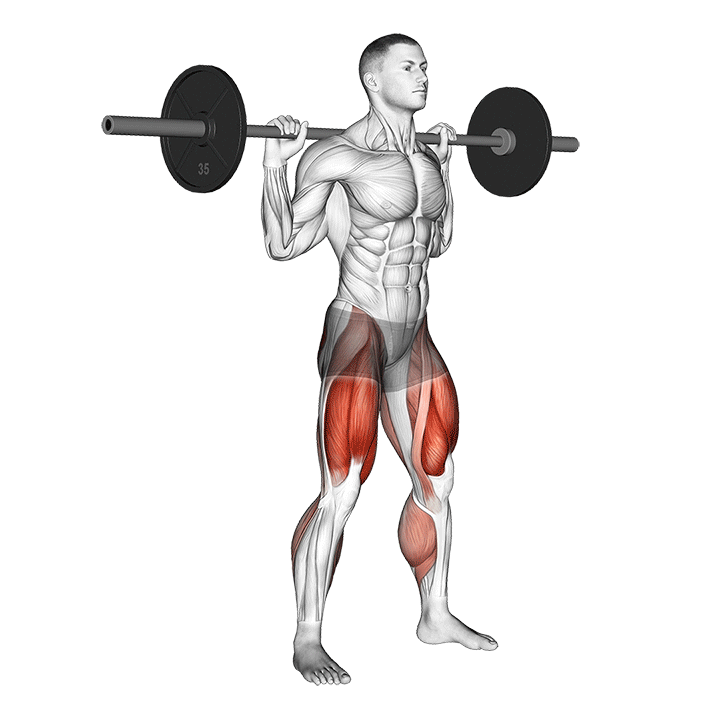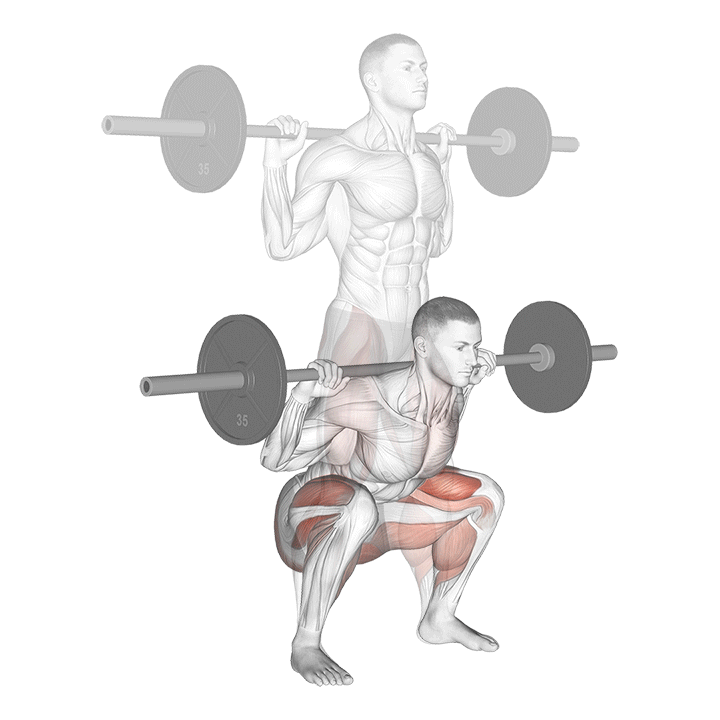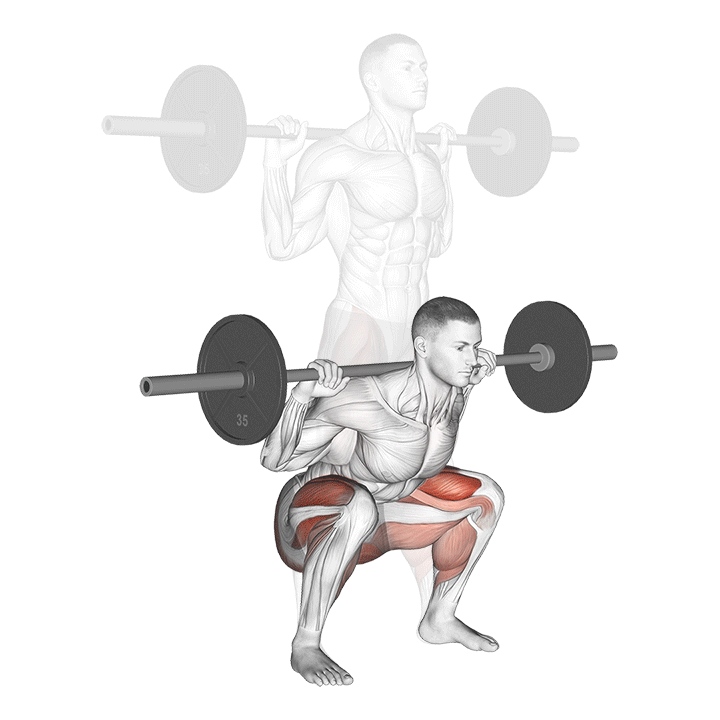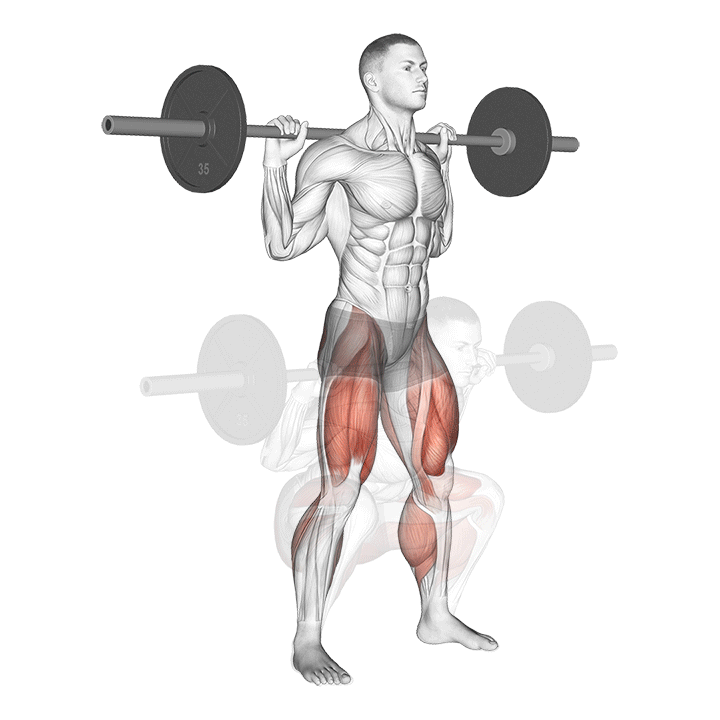
- STEP 1 – Start with the barbell endorsed on top of the traps.
- STEP 2 –The chest must be up and the head fronting forward.
- STEP 3 – Embrace a hip-width posture with the feet turned out as needed.
- STEP 4 – Dismount by bending the knees, abstaining from moving the hips back as much as feasible. This demands that the knees travel forward. Confirm that they stay parallel with the feet. The purpose is to keep the body as erect as you can.
- STEP 5 – Continue down, maintaining the weight on the front of the heel. At the moment the upper legs reach the lower legs change the motion, moving the weight upward.
How to improve your squats?
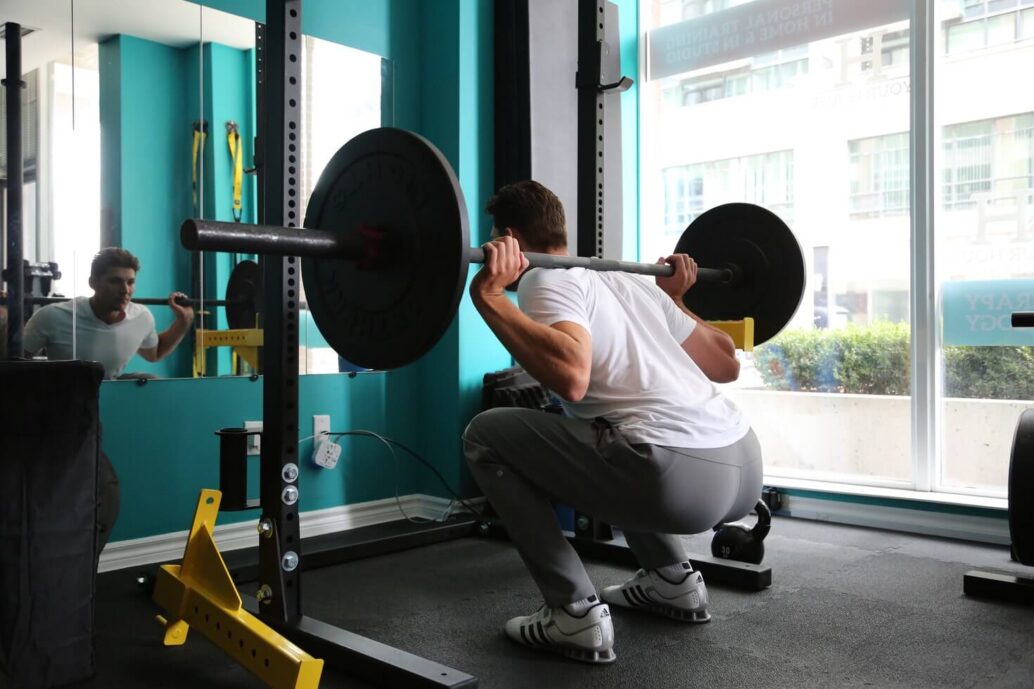

There are some safety precautions that you must keep in mind when doing squats are discussed here. Only decline yourself as far as you can easily do. When you start to feel distressed in your hips or knees, stop and use that as your endpoint.
Ensure you have stable ground. Most squat exercises demand you to begin with your feet a little wider than shoulder-width apart. Using a thinner posture lets you target the outer thigh muscles, but it also reduces the strength of your floor and puts extra stress on your knees.
Keep your eyes forward. While it may appear natural to look down when performing a squat, you need to keep your eyes straight ahead. To do this, you need to pick a place in front of you to concentrate on. This may help you maintain your neck in an unbiased position. Keep your stance upright. Evade rounding your back or shoulders. Concentrate on keeping your spine straight and in an impartial position, with your head neutral, not looking up or down.
Only lift what you can handle. Avoid going heavy with a weight if your state can’t bear it. You will benefit more from the squat if you manage it with good form than you will if you lift too much weight. Apart from this, lifting too much weight can weaken your lower back, hips, and knees, which can direct to damage. Activate your body. Keep your body muscles triggered throughout the whole movement. Think of these muscles as your inner weight belt that carries everything in its position.
Benefits of Squats
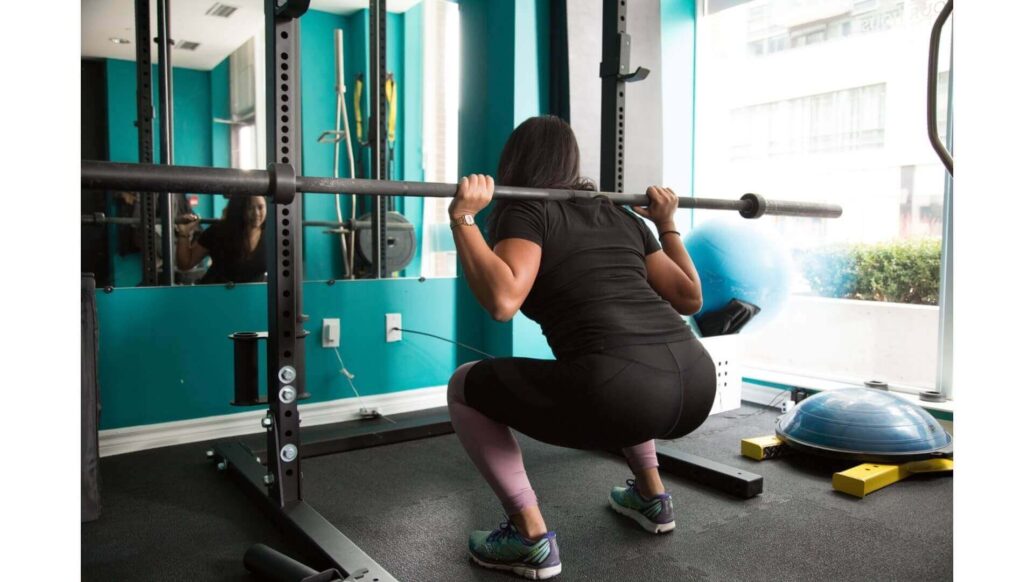

Professionals consider the squat as one of the most useful exercises for improving athletic routine. It is moderately comfortable for most people to perform because it does not demand any equipment.
The specific advantages to the body include:
- strengthening the muscles in the legs that includes the calves, quadriceps, and hamstrings
- supporting the knee joint
- burning fat and boosting weight loss
- maintaining the lower back
- enhancing flexibility in the lower body


